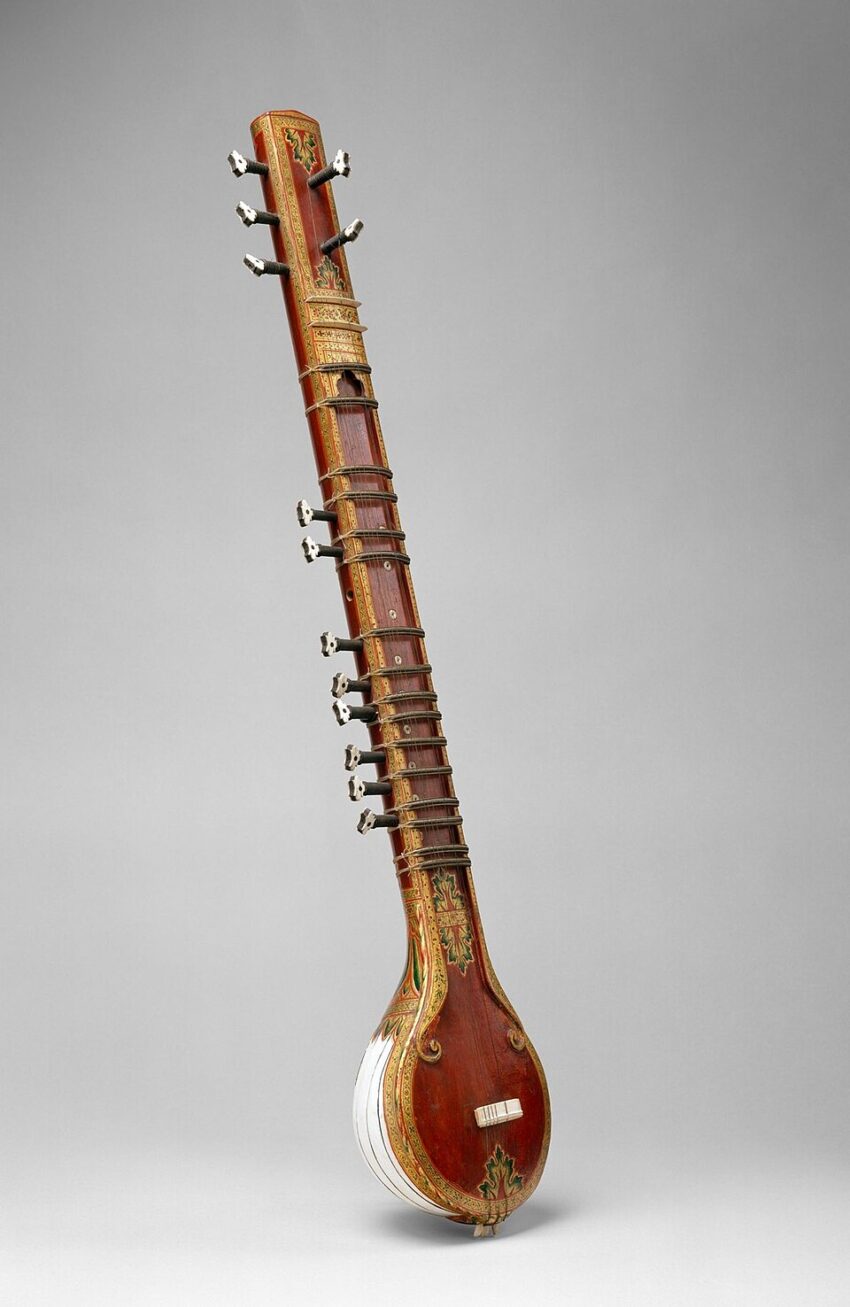
Q1. What is the primary musical tradition in which the sitar is predominantly used?
A. Carnatic classical music
B. Hindustani classical music
C. Sufi devotional music
D. Folk music of South India
Answer: B. Hindustani classical music
Q2. The sitar is believed to have evolved from which ancient Indian instrument?
A. Tanpura
B. Sarod
C. Veena
D. Tabla
Answer: C. Veena
Q3. Approximately how many strings does a standard sitar have in total?
A. 7-10
B. 11-13
C. 18-21
D. 25-30
Answer: C. 18-21
Q4. Which part of the sitar is the large gourd resonator at the bottom?
A. Tabli
B. Dand
C. Gulu
D. Tumba
Answer: D. Tumba
Q5. The sympathetic strings on a sitar, known as tarab, primarily serve to:
A. Play the main melody
B. Provide rhythmic accompaniment
C. Act as drone strings
D. Resonate in sympathy to create overtones
Answer: D. Resonate in sympathy to create overtones
Q6. What is the name of the wire plectrum worn on the finger to pluck the sitar strings?
A. Mizrab
B. Jawari
C. Chikari
D. Parda
Answer: A. Mizrab
Q7. Which famous sitar maestro is widely credited with popularizing the sitar in the West during the 1950s and 1960s?
A. Vilayat Khan
B. Nikhil Banerjee
C. Ravi Shankar
D. Anoushka Shankar
Answer: C. Ravi Shankar
Q8. The sitar’s bridge, responsible for its characteristic buzzing sound, is adjusted in a process called:
A. Tuninghe chikari
B. Setting the jawari
C. Adjusting the parda
D. Balancing the tumba
Answer: B. Setting the jawari
Q9. In sitar playing, what technique involves pulling the string sideways to bend notes and create glides?
A. Gamak
B. Taan
C. Krintan
D. Meend
Answer: D. Meend
Q10. Which Beatles song first prominently featured the sitar, played by George Harrison?
A. Yesterday
B. Within You Without You
C. Norwegian Wood (This Bird Has Flown)
D. Hey Jude
Answer: C. Norwegian Wood (This Bird Has Flown)
Q11. The sitar typically has movable frets made of metal tied to the neck with strings; these are called:
A. Pardas
B. Kuntis
C. Tarabs
D. Ghorajs
Answer: A. Pardas
Q12. Which gharana is associated with the gayaki ang style, imitating vocal nuances on the sitar?
A. Maihar gharana
B. Imdadkhani (Etawah) gharana
C. Jaipur gharana
D. Bishnupur gharana
Answer: B. Imdadkhani (Etawah) gharana
Q13. The chikari strings on a sitar are primarily used for:
A. Sympathetic resonance
B. Bass notes
C. Drone and rhythmic emphasis
D. Main melodic playing
Answer: C. Drone and rhythmic emphasis
Q14. Who is a prominent contemporary sitar player and daughter of Ravi Shankar?
A. Shubha Mudgal
B. Anoushka Shankar
C. Kishori Amonkar
D. Annapurna Devi
Answer: B. Anoushka Shankar
Q15. Which instrument is a drone accompaniment often paired with the sitar, but has no frets?
A. Sarod
B. Veena
C. Tanpura
D. Surbahar
Answer: C. Tanpura
Q16. The Kharaj Pancham style of sitar tuning, popularized by Ravi Shankar, includes:
A. No bass strings
B. Low Sa and low Pa strings
C. Extra Gandhar chikari
D. Only sympathetic strings
Answer: B. Low Sa and low Pa strings
Q17. Which sitar maestro was known for the Gandhar Pancham style and belonged to the Imdadkhani gharana?
A. Ravi Shankar
B. Allauddin Khan
C. Nikhil Banerjee
D. Vilayat Khan
Answer: D. Vilayat Khan
Q18. The long hollow neck of the sitar is referred to as:
A. Tumba
B. Gulu
C. Dand
D. Tabli
Answer: C. Dand
Q19. In the 1960s, electric versions of the sitar were popularized in Western music, such as the:
A. Coral Sitar by Danelectro
B. Fender Sitar
C. Gibson Veena
D. Yamaha Tanpura
Answer: A. Coral Sitar by Danelectro
Q20. Which part connects the neck to the main resonator on some sitars?
A. Jawari
B. Parda
C. Gulu
D. Chota ghoraj
Answer: C. Gulu
Q21. The Maihar gharana, associated with Ravi Shankar, traces its lineage to:
A. Imdad Khan
B. Allauddin Khan
C. Amir Khusro
D. Tansen
Answer: B. Allauddin Khan
Q22. What is the typical playing position for a sitar?
A. Standing with a strap
B. Held vertically like a cello
C. Sitting cross-legged with the tumba on the foot
D. Placed on a stand
Answer: C. Sitting cross-legged with the tumba on the foot
Q23. The sarod differs from the sitar mainly by having:
A. No frets and a metal fingerboard
B. More sympathetic strings
C. A larger tumba
D. Wooden plectrum
Answer: A. No frets and a metal fingerboard
Q24. Which innovation is credited to the Imdadkhani gharana?
A. Adding low bass strings
B. Introducing jawari adjustment
C. Creating the electric sitar
D. Developing gayaki ang on sitar
Answer: D. Developing gayaki ang on sitar
Q25. The sitar’s wood is commonly made from:
A. Mahogany
B. Toon or teak
C. Rosewood only
D. Bamboo
Answer: B. Toon or teak