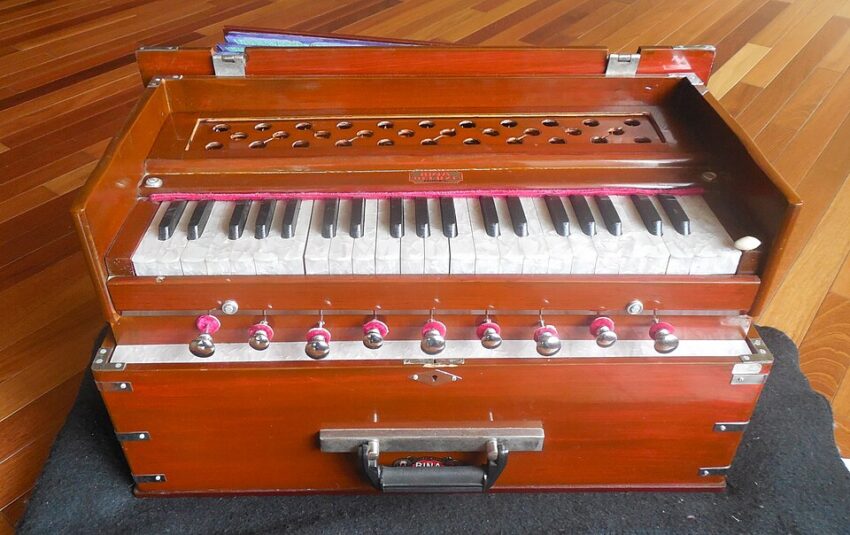
Q1. Who is credited with patenting and naming the instrument “harmonium” in 1840?
A. Christian Gottlieb Kratzenstein
B. Alexandre Debain
C. Dwarkanath Ghose
D. Victor Mustel
Answer: B. Alexandre Debain
Q2. The harmonium produces sound through which mechanism?
A. Struck strings like a piano
B. Bowed strings like a violin
C. Air vibrating metal free reeds
D. Plucked reeds like a harp
Answer: C. Air vibrating metal free reeds
Q3. What adaptation made the harmonium suitable for Indian musicians sitting on the floor?
A. Foot pedals
B. Hand-pumped bellows
C. Electric pump
D. Larger keyboard
Answer: B. Hand-pumped bellows
Q4. Which part of the harmonium is pumped to supply air to the reeds?
A. Stops
B. Keyboard
C. Bellows
D. Drone knobs
Answer: C. Bellows
Q5. In Indian harmoniums, what are “stops” primarily used for?
A. Controlling airflow to reed banks for timbre and volume
B. Changing the scale
C. Producing drone notes
D. Tuning the reeds
Answer: A. Controlling airflow to reed banks for timbre and volume
Q6. Why was the harmonium banned on All India Radio from 1940 to 1971?
A. It was too expensive
B. Lack of popularity
C. Inability to produce glides (meend) and oscillations (gamaka), plus foreign origin
D. Excessive noise
Answer: C. Inability to produce glides (meend) and oscillations (gamaka), plus foreign origin
Q7. Which feature was added to Indian harmoniums to support classical music?
A. Foot pedals
B. Drone stops
C. Electric amplification
D. 88 keys
Answer: B. Drone stops
Q8. The Indian harmonium is most commonly used in which musical tradition?
A. Western classical
B. Jazz improvisation
C. Hindustani classical accompaniment
D. Rock music
Answer: C. Hindustani classical accompaniment
Q9. Who developed a 22-shruti harmonium for better microtonal play in Indian music?
A. Alexandre Debain
B. Vidyadhar Oke
C. Dwarkanath Ghose
D. Tulsidas Borkar
Answer: B. Vidyadhar Oke
Q10. What is a “scale changer” harmonium?
A. Allows transposing without changing fingering
B. One with foot pedals
C. Keyless for drones only
D. With built-in swarmandal strings
Answer: A. Allows transposing without changing fingering
Q11. Which famous Indian musician called the harmonium the “bane of Indian music”?
A. Bhimsen Joshi
B. Rabindranath Tagore
C. Nusrat Fateh Ali Khan
D. Kishori Amonkar
Answer: B. Rabindranath Tagore
Q12. The harmonium is classified as which type of instrument?
A. String (chordophone)
B. Membrane (membranophone)
C. Free-reed aerophone
D. Idiophone
Answer: C. Free-reed aerophone
Q13. Which renowned harmonium player accompanied vocalists like Bhimsen Joshi and Kishori Amonkar?
A. Krishna Das
B. Vidyadhar Oke
C. Jai Uttal
D. Pandit Tulsidas Borkar
Answer: D. Pandit Tulsidas Borkar
Q14. In harmonium playing, what does pumping the bellows control?
A. Dynamics and sustain
B. Pitch
C. Tempo
D. Key signature
Answer: A. Dynamics and sustain
Q15. What is a “shruti box”?
A. A full-keyboard harmonium
B. A keyless harmonium for drones only
C. A foot-pumped Western version
D. A scale-changing model
Answer: B. A keyless harmonium for drones only
Q16. The Western harmonium often uses which pumping method?
A. Hand only
B. Electric
C. Foot pedals
D. Mouth-blown
Answer: C. Foot pedals
Q17. Which harmonium player is known for elevating it to solo concert status in Hindustani music?
A. Appa Jalgaonkar
B. Alexandre Debain
C. Jacob Estey
D. Lionel Fielden
Answer: A. Appa Jalgaonkar
Q18. What limitation of the harmonium affects its use in pure Indian classical music?
A. Too loud
B. Fixed equal temperament and no continuous glides
C. Too heavy
D. Limited range
Answer: B. Fixed equal temperament and no continuous glides
Q19. Drone notes on an Indian harmonium are typically which swaras?
A. Ga and Ma
B. Ni and Ti
C. Re and Dha
D. Sa and Pa
Answer: D. Sa and Pa
Q20. Who introduced the harmonium to India?
A. Indian craftsmen independently
B. European missionaries and traders
C. American manufacturers
D. Chinese traders
Answer: B. European missionaries and traders
Q21. Which material are harmonium reeds typically made of?
A. Wood
B. Plastic
C. Brass or steel
D. Bamboo
Answer: C. Brass or steel
Q22. A “coupler” in some harmoniums does what?
A. Changes scale
B. Adds octave above or below
C. Controls bellows
D. Tunes drones
Answer: B. Adds octave above or below
Q23. Famous qawwali artist Nusrat Fateh Ali Khan often used harmonium for what?
A. Solo performances only
B. Drone only
C. Accompaniment in Sufi music
D. Percussion
Answer: C. Accompaniment in Sufi music
Q24. What is the typical octave range of a standard Indian portable harmonium?
A. 7 octaves like a piano
B. 3 to 4 octaves
C. 1 octave
D. 5 octaves
Answer: B. 3 to 4 octaves
Q25. Which harmonium variant includes plucked strings like a swarmandal?
A. Samvadini
B. Standard
C. Shruti box
D. Scale changer
Answer: A. Samvadini