Q1. What is the primary sound production mechanism of the celesta?
A. Vibrating strings struck by hammers
B. Metal bars struck by felt hammers
C. Tuning forks vibrated by keys
D. Wooden plates bowed with a mechanism
Answer: B. Metal bars struck by felt hammers
Q2. The name “celesta” derives from a French word meaning what?
A. Bell-like
B. Sparkling
C. Heavenly
D. Mystic
Answer: C. Heavenly
Q3. In which year was the modern celesta patented?
A. 1860
B. 1886
C. 1892
D. 1900
Answer: B. 1886
Q4. Who is credited with inventing the celesta?
A. Auguste Mustel
B. Victor Mustel
C. Charles Mustel
D. Alphonse Mustel
Answer: A. Auguste Mustel
Q5. The celesta is classified as which type of instrument in the Hornbostel-Sachs system?
A. Chordophone
B. Aerophone
C. Idiophone
D. Membranophone
Answer: C. Idiophone
Q6. Which famous ballet features the celesta prominently in the “Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy”?
A. Swan Lake
B. The Sleeping Beauty
C. Romeo and Juliet
D. The Nutcracker
Answer: D. The Nutcracker
Q7. Which composer is often credited with popularizing the celesta in orchestral music through The Nutcracker?
A. Gustav Mahler
B. Maurice Ravel
C. Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
D. Gustav Holst
Answer: C. Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
Q8. The celesta is a transposing instrument that sounds how many octaves higher than written?
A. One octave lower
B. One octave higher
C. The same as written
D. Two octaves higher
Answer: B. One octave higher
Q9. Which instrument is considered the closest relative to the celesta but produces a brighter, more piercing sound?
A. Glockenspiel
B. Vibraphone
C. Xylophone
D. Marimba
Answer: A. Glockenspiel
Q10. Larger celesta models (four or five octaves) typically include what feature for controlling sustain?
A. Una corda pedal
B. Damper pedal
C. Soft pedal only
D. No pedal
Answer: B. Damper pedal
Q11. In Gustav Holst’s orchestral suite The Planets, the celesta is prominently featured in which movement?
A. Mars, the Bringer of War
B. Jupiter, the Bringer of Jollity
C. Neptune, the Mystic
D. Venus, the Bringer of Peace
Answer: C. Neptune, the Mystic
Q12. Which composer used the celesta extensively in symphonies such as No. 6 and No. 8?
A. Igor Stravinsky
B. Gustav Mahler
C. Claude Debussy
D. Richard Strauss
Answer: B. Gustav Mahler
Q13. The celesta’s timbre is often described as similar to a glockenspiel but with what key difference?
A. Softer and more subtle
B. Louder and more piercing
C. Deeper and resonant
D. Brighter and metallic
Answer: A. Softer and more subtle
Q14. In orchestral seating, the celesta is typically grouped with which section?
A. Strings
B. Brass
C. Woodwinds
D. Percussion or keyboards
Answer: D. Percussion or keyboards
Q15. Which film score series prominently features the celesta in “Hedwig’s Theme”?
A. Star Wars
B. The Lord of the Rings
C. Harry Potter
D. Indiana Jones
Answer: C. Harry Potter
Q16. The predecessor to the celesta, invented by Victor Mustel, was called what?
A. Dulcitone
B. Typophone
C. Keyboard glockenspiel
D. Bell-piano
Answer: B. Typophone
Q17. Modern professional celestas often have a range of how many octaves?
A. Four to five and a half octaves
B. Three octaves
C. Six octaves
D. Two octaves
Answer: A. Four to five and a half octaves
Q18. Which manufacturer is known for producing celestas strictly according to the original Mustel mechanism?
A. Yamaha
B. Kolberg
C. Schiedmayer
D. Bergerault
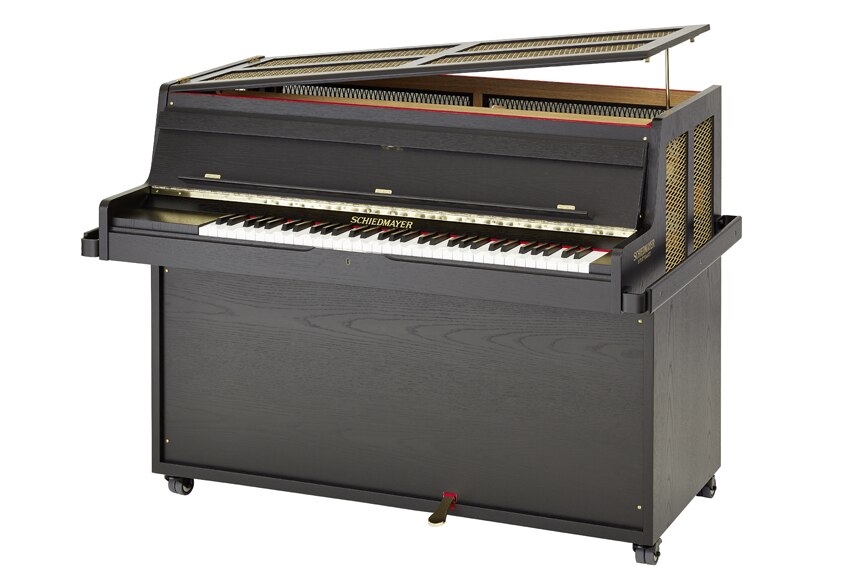
Answer: C. Schiedmayer
Q19. The celesta is often used in music to evoke feelings of what?
A. Aggression and power
B. Mystery, magic, or dreaminess
C. Sadness and melancholy
D. Joy and celebration
Answer: B. Mystery, magic, or dreaminess
Q20. Who reportedly used the celesta before Tchaikovsky in incidental music for Shakespeare’s The Tempest?
A. Ernest Chausson
B. Maurice Ravel
C. Karol Szymanowski
D. Bela Bartok
Answer: A. Ernest Chausson
Q21. In Bartok’s Music for Strings, Percussion and Celesta, the instrument is featured in which capacity?
A. Solo throughout
B. Prominently in demanding parts
C. Only in the finale
D. Minimally for color
Answer: B. Prominently in demanding parts
Q22. The hammers in a celesta are typically covered with what material?
A. Hard plastic
B. Metal
C. Felt
D. Wood
Answer: C. Felt
Q23. Wooden resonators in the celesta serve to do what?
A. Dampen the sound
B. Change the pitch
C. Produce overtones only
D. Amplify and warm the tone
Answer: D. Amplify and warm the tone
Q24. Tchaikovsky first encountered the celesta during a trip to which city?
A. London
B. Vienna
C. Paris
D. Berlin
Answer: C. Paris
Q25. The celesta is sometimes substituted for which older instrument in performances of Mozart’s The Magic Flute?
A. Harpsichord
B. Keyboard glockenspiel
C. Organ
D. Harp
Answer: B. Keyboard glockenspiel