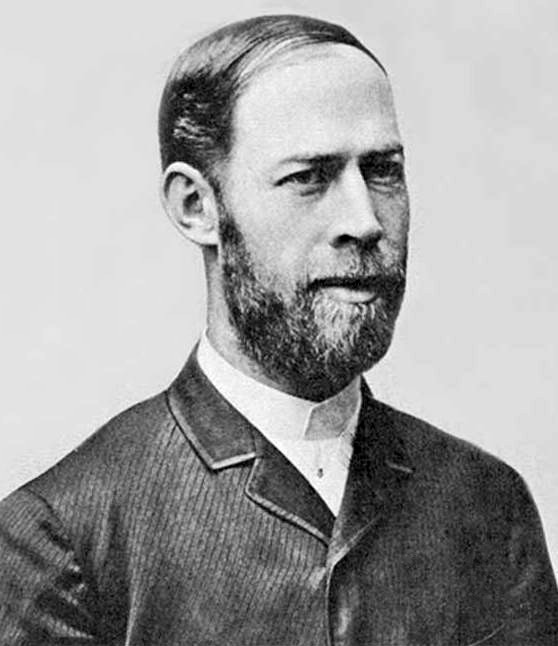
Heinrich Hertz Quiz Questions
1. Heinrich Hertz was a renowned physicist from:
(a) France
(b) Germany
(c) Italy
(d) England
2. Hertz is best known for his discovery of:
(a) Gravity
(b) Electricity
(c) Radio waves
(d) X-rays
3. The unit of frequency is named after:
(a) Albert Einstein
(b) Isaac Newton
(c) Heinrich Hertz
(d) James Maxwell
4. Hertz’s experiments were conducted in the late:
(a) 17th century
(b) 18th century
(c) 19th century
(d) 20th century
5. Hertz’s discovery of radio waves was a crucial step in the development of:
(a) Television
(b) Computers
(c) Radio
(d) All of the above
6. Hertz’s work was based on the theoretical predictions of:
(a) Thomas Edison
(b) James Clerk Maxwell
(c) Nikola Tesla
(d) Alexander Graham Bell
7. Hertz used a device called a ** to generate and detect radio waves.
(a) Tesla coil
(b) Hertzian oscillator
(c) Marconi transmitter
(d) De Forest audion tube
8. Hertz’s experiments were conducted in the city of:
(a) Karlsruhe
(b) Munich
(c) Hamburg
(d) Bonn
9. Hertz’s work was crucial for the development of:
(a) Radar
(b) Television
(c) Radio
(d) All of the above
10. Hertz’s experiments helped to confirm Maxwell’s theory of:
(a) Electromagnetism
(b) Relativity
(c) Quantum mechanics
(d) Thermodynamics
11. Hertz died at the relatively young age of:
(a) 25
(b) 36
(c) 47
(d) 58
12. Hertz’s experiments were conducted in:
(a) A laboratory
(b) A basement
(c) A field
(d) A classroom
13. Hertz’s discovery of radio waves was a major breakthrough in:
(a) Physics
(b) Chemistry
(c) Biology
(d) Astronomy
14. Hertz’s discovery of radio waves was a significant contribution to the field of:
(a) Electromagnetism
(b) Optics
(c) Acoustics
(d) Fluid mechanics
15. Heinrich Hertz was a:
(a) Physicist
(b) Chemist
(c) Biologist
(d) Astronomer
16. What device did Hertz use to generate and detect radio waves?
(a) A telescope
(b) A spark gap transmitter
(c) A steam engine
(d) A battery
17. Heinrich Hertz’s experiments helped to confirm:
(a) Newton’s laws of motion
(b) Einstein’s theory of relativity
(c) Maxwell’s equations
(d) Dalton’s atomic theory
18. Which of the following is an example of an electromagnetic wave?
(a) Sound
(b) Heat
(c) Light
(d) Water
19. Electromagnetic waves are classified based on their:
(a) Mass
(b) Charge
(c) Velocity
(d) Frequency
20. Which of the following is not an electromagnetic wave?
(a) Gamma rays
(b) X-rays
(c) Ultraviolet rays
(d) Gravitational waves
21. Heinrich Hertz died in:
(a) 1887
(b) 1894
(c) 1901
(d) 1918
22. The speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum is:
(a) 3 x 10^5 m/s
(b) 3 x 10^8 m/s
(c) 3 x 10^11 m/s
(d) 3 x 10^14 m/s
23. The wavelength of an electromagnetic wave is related to its:
(a) Frequency
(b) Amplitude
(c) Velocity
(d) Polarization
24. Heinrich Hertz was a professor at the University of:
(a) Bonn
(b) Berlin
(c) Munich
(d) Karlsruhe
25. The electromagnetic spectrum includes:
(a) Radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays
(b) Only visible light
(c) Only radio waves and microwaves
(d) Only X-rays and gamma rays
Heinrich Hertz Quiz Questions with Answers
1. Heinrich Hertz was a renowned physicist from:
(b) Germany
2. Hertz is best known for his discovery of:
(c) Radio waves
3. The unit of frequency is named after:
(c) Heinrich Hertz
4. Hertz’s experiments were conducted in the late:
(c) 19th century
5. Hertz’s discovery of radio waves was a crucial step in the development of:
(d) All of the above
6. Hertz’s work was based on the theoretical predictions of:
(b) James Clerk Maxwell
7. Hertz used a device called a ** to generate and detect radio waves.
(b) Hertzian oscillator
8. Hertz’s experiments were conducted in the city of:
(a) Karlsruhe
9. Hertz’s work was crucial for the development of:
(d) All of the above
10. Hertz’s experiments helped to confirm Maxwell’s theory of:
(a) Electromagnetism
11. Hertz died at the relatively young age of:
(b) 36
12. Hertz’s experiments were conducted in:
(a) A laboratory
13. Hertz’s discovery of radio waves was a major breakthrough in:
(a) Physics
14. Hertz’s discovery of radio waves was a significant contribution to the field of:
(a) Electromagnetism
15. Heinrich Hertz was a:
(a) Physicist
16. What device did Hertz use to generate and detect radio waves?
(b) A spark gap transmitter
17. Heinrich Hertz’s experiments helped to confirm:
(c) Maxwell’s equations
18. Which of the following is an example of an electromagnetic wave?
(c) Light
19. Electromagnetic waves are classified based on their:
(d) Frequency
20. Which of the following is not an electromagnetic wave?
(d) Gravitational waves
21. Heinrich Hertz died in:
(b) 1894
22. The speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum is:
(b) 3 x 10^8 m/s
23. The wavelength of an electromagnetic wave is related to its:
(c) Velocity
24. Heinrich Hertz was a professor at the University of:
(d) Karlsruhe
25. The electromagnetic spectrum includes:
(a) Radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays